
Camouflage
Camouflage
Kingdom Animalia includes diverse species with genetic and structural similarities.
Learning Objective: Demonstrate the effectiveness of camouflage as a tool for prey species.

Camouflage sounds simple: blending in with your surroundings. But this section will demonstrate that there are diverse forms of camouflage that address particular threats.
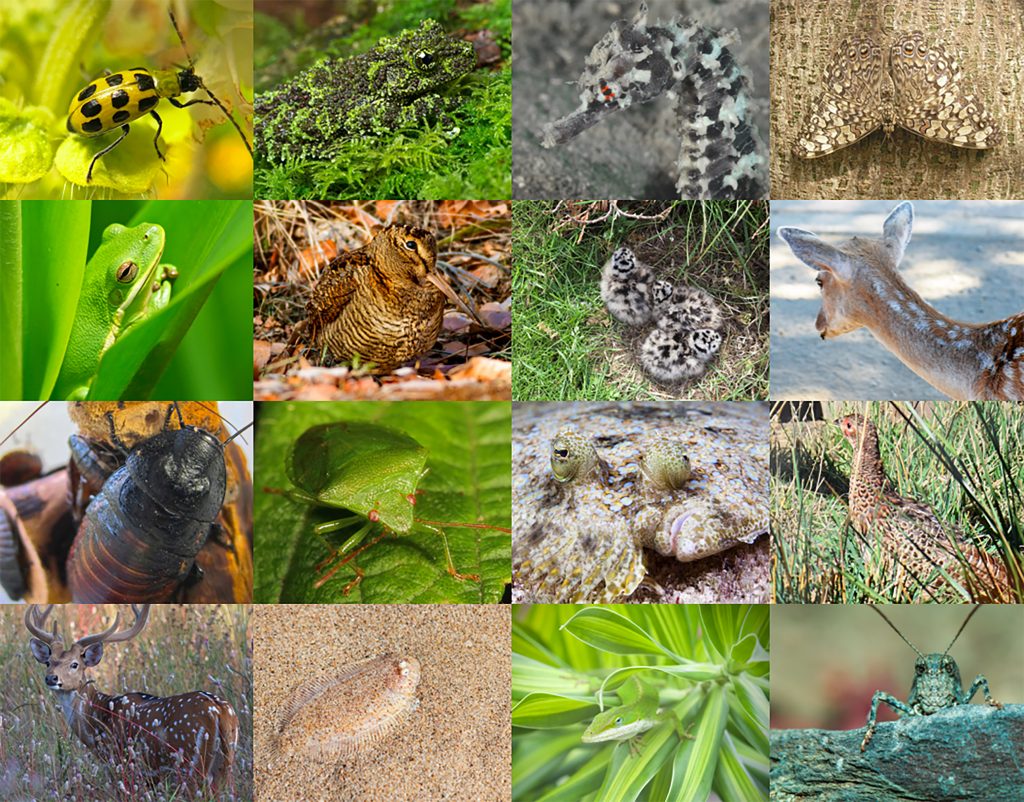

Patterns mimicking shade and dappled light enable even large organisms to blend into their surroundings.
Vertical striping can enable herbivores to blend into grass fields, or make it difficult to discern between individuals in a herd.

Vertical striping patterns enable these fish to blend with aquatic plants and algae.
Iridescence in fish and insects may make it difficult for predators to follow prey as they move from light to shadow.
Countershading, different colors on the top and bottom of an animal, allows it to blend with sky from one angle, and ground or water from the other.
Note how color, pattern, and reduced movement work together to camouflage these species.
Some insect species flash a bright color when they are approached by a predator. This may temporarily startle the predator, enabling the insect to escape. These are two different moth species that “flash and startle.”

Moth adults and larvae (caterpillars have a variety of forms of camouflage. This video introduces “eye spots.”
A photo of eyespots on a butterflyfish and the Io moth.

Taking it a step further, these caterpillars have abdomens that look like false snake heads. They can even inflate them to look more menacing.

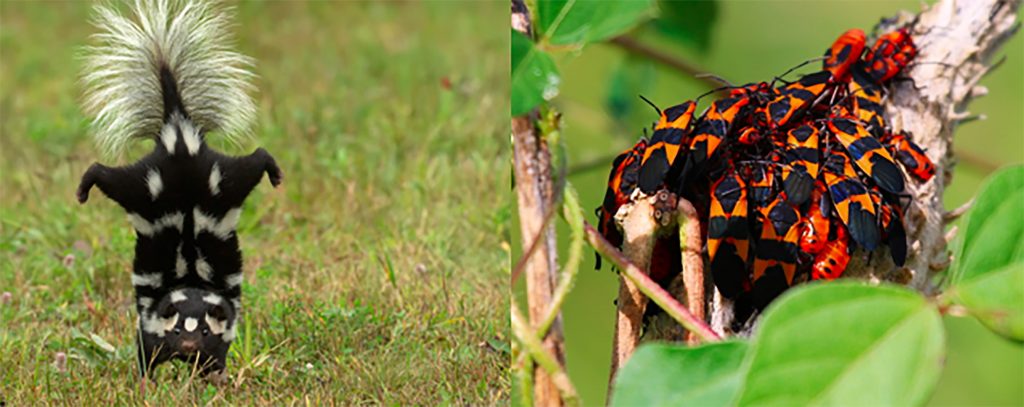
Some species, including this skunk and milkweed bugs use bold colors to warn away potential predators. Bright colors can indicate chemical toxins are present.


Another option is to mimic something a predator is not likely to eat. This hoverfly looks like a bee, and is less likely to be eaten by birds. If this hoverfly survives and reproduces, it has a high level of fitness due to its appearance.
The species on the left is unpalatable and unlikely to be eaten by birds. The species on the right is a mimic: it looks similar enough to the other species, birds will not eat this one either.


Humans have adopted the idea of mimicry to develop new materials and services.
Biomimicry is designing products that are based on structures found in nature.
Understanding how animal structures relate to their functions has led to the development of human products, a clear connection between science and other fields of study.











