Genes Parts of DNA that Code for Proteins


Genes Outcomes
-
Explain what a gene is and how it relates to DNA.
-
Describe the process of transcription, including where it occurs and what is produced.
-
Describe the process of translation, including where it occurs and what is produced.
There are questions scattered throughout the resources; these are examples of the types of questions that could appear on Monday\’s quiz that covers all of this week\’s material (lectures, labs, and these online resource pages).
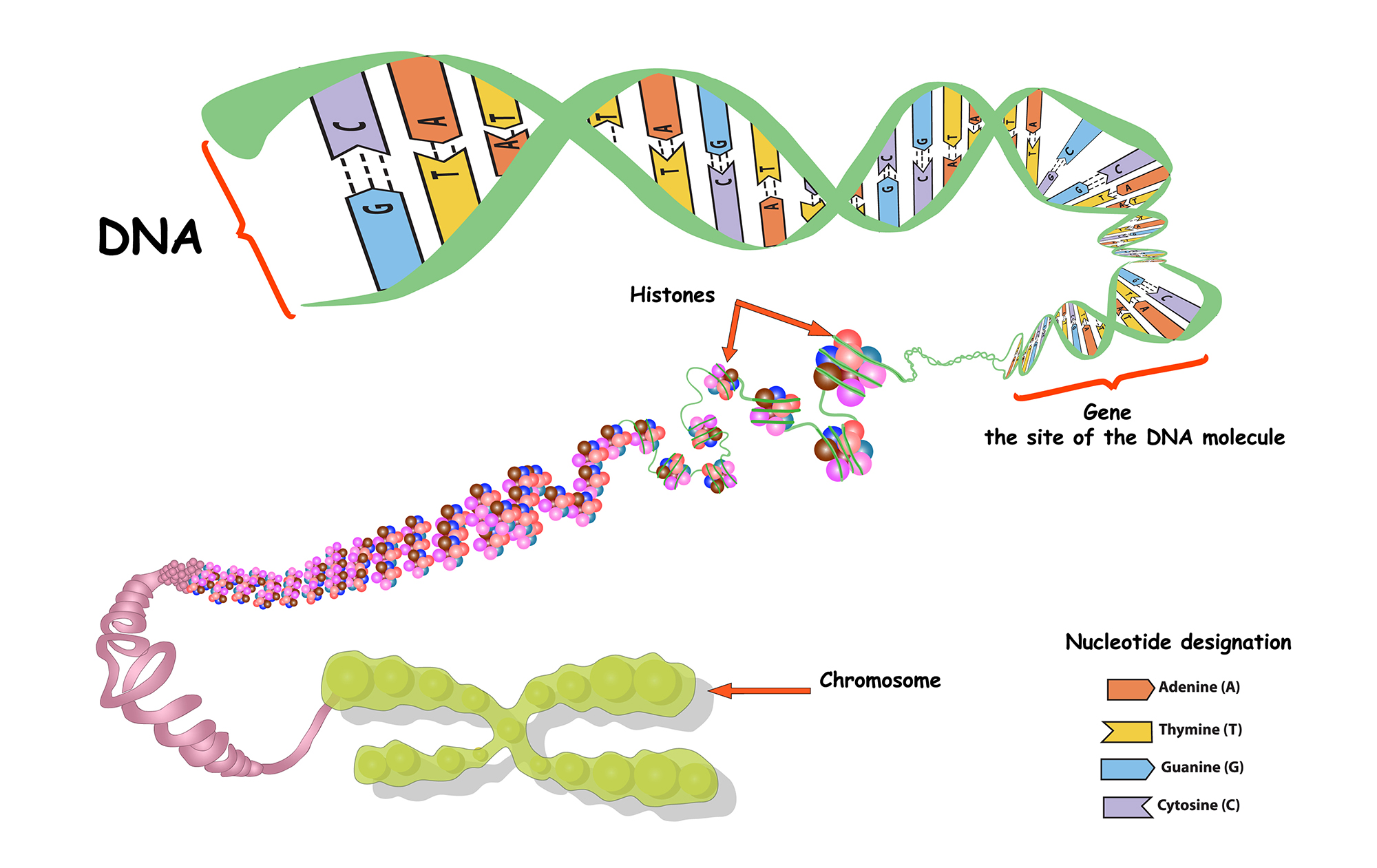
Chromosomes are coiled DNA wrapped around histone proteins. These proteins keep the long DNA macromolecule from \”tangling.\” These proteins are not the substance of heredity; it is the DNA molecule that has the code for purple vs. white flower color, or a fruit fly vs. a pea plant.
From class, a nucleotide in DNA consists of one of the four bases (A, T, C, G) combined with a _____ and a _____ (represented by the green lines in this image).
Genes are sequences of DNA that code for _____.
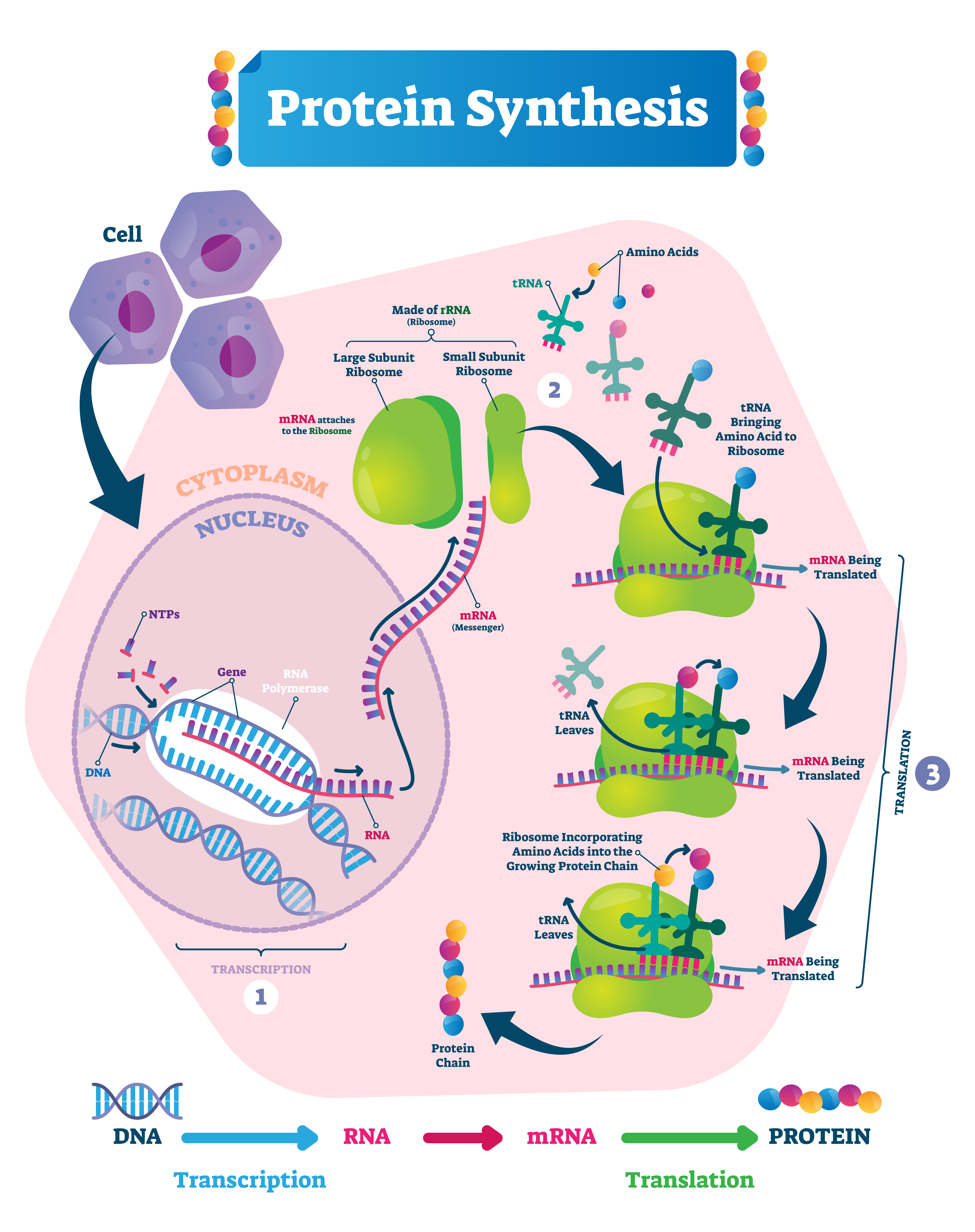
This page explores how the DNA code, the order of C-T-G-A bases, related to cells making proteins, also called the process of protein synthesis.
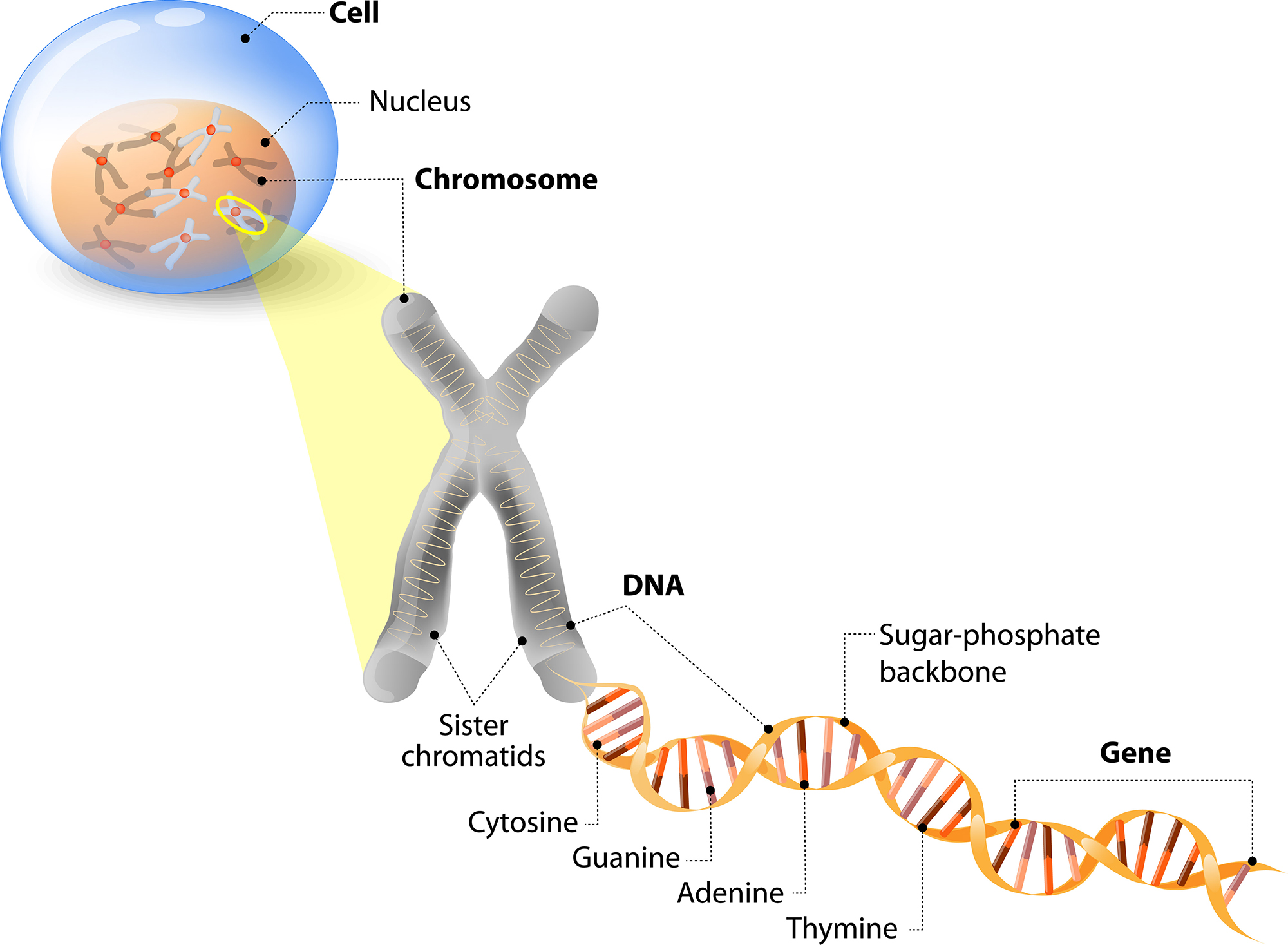
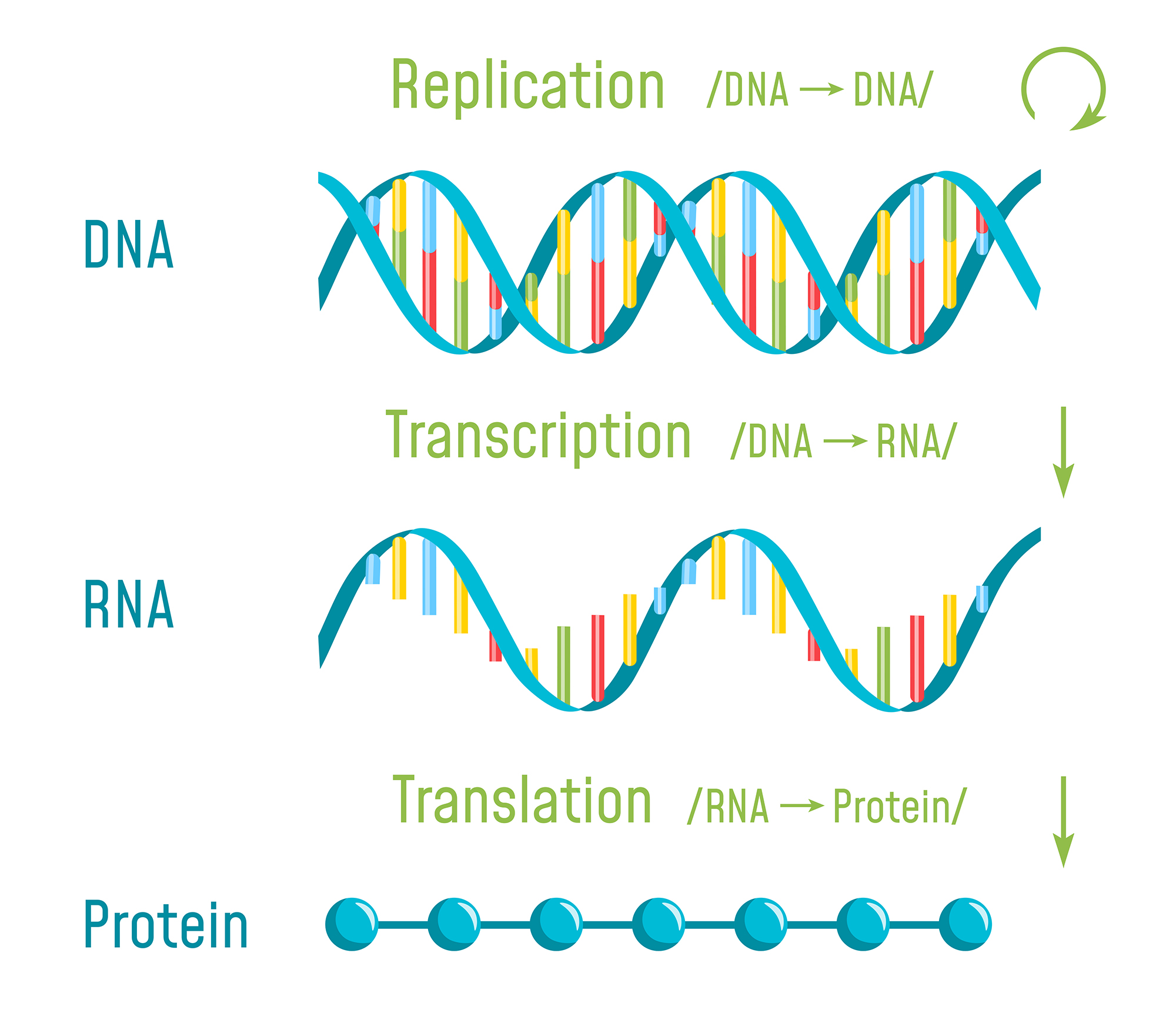
The basic processes that involve DNA are:
Replication: Making a new, identical chromosome for mitosis or meiosis. Meiosis results in production of gametes, which in humans are _____ from the testes or _____ from the ovaries.
Transcription: Making an RNA copy of a portion of DNA. List two ways the structure of RNA differs from the structure of DNA.
Translation: RNA directing the correct order of amino acids in a polypeptide. A poypeptide is a chain of ________; and the polypeptide is folded to make a _______.
This video demonstrates protein synthesis; making a polypeptide chain of amino acids.
Key terminology is defined below this video.
Key Terminology
Nucleotide: a phosphate, sugar, and a base.
Codon: three nucleotides together, codes for a single amino acid.
Genetic Code: the same codon sequence codes for the same amino acid, no matter which species.
mRNA: messenger RNA is a copy of a gene region of DNA.
rRNA: ribosomal RNA makes up the ribosome structure.
tRNA: transfer RNA brings the correct amino acid to the corresponding mRNA codon.
If you would like to see the protein synthesis puzzle from lab again, watch this video:
Check your knowledge. Can you:
-
explain what a gene is and how it relates to DNA?
-
describe the process of transcription, including where it occurs and what is produced?
-
describe the process of translation, including where it occurs and what is produced?