
Eyes
Eyes
There are remarkable similarities and differences in animal eyes. This section explores the evolutionary pathway of eye structure and function.
Learning Objective: Diagram basic eye structure and note significant evolutionary changes over time.
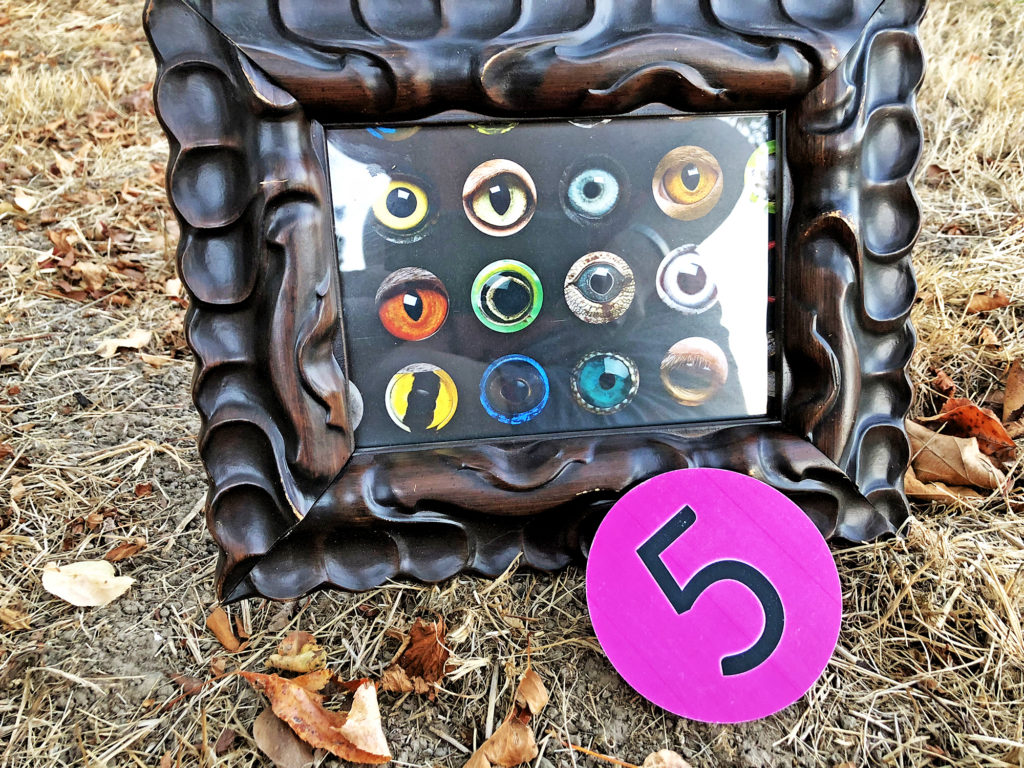


Eyes are critical in collecting information that can assist animals in finding food, locating mates, evading predators, determining location, and time of day.
Animal eyes vary significantly, and visual abilities relate to the number, quality, and arrangement of light-sensitive cells.

Most invertebrates have light sensitive cells that can sense ambient light and directionality of a light source.
Most vertebrates and some mollusks contain light-sensitive cells within a protective retina, often with structures that focus light to produce crisp images.
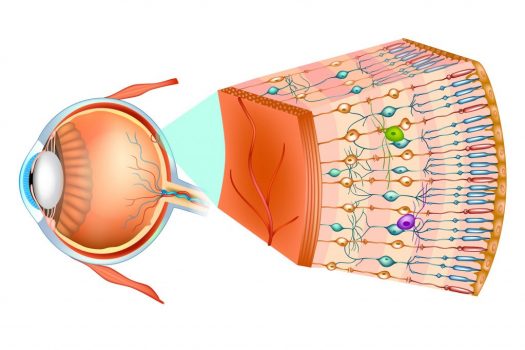
Humans share basic eye structure with many other vertebrates. This video provides information on human eye structures and how they relate to vision.
Watch this video; you can select the closed captioning “cc” option if you would like to see the text.
Eye structures relate to function.

These cave tetras (Anoptichthys jordani) no longer have eyes in their eye sockets. In environments where vision is no longer necessary, like caves, some animal species lose visual function over many generations as mutations accumulate.
These two sibling guinea pigs have different eye colors: red and black. The lack of melanin pigment in the red-eyed guinea pig increases the light that reaches the retina. In some species, this leads to higher mutational damage of retinal cells when exposed to high light.
Small cats species have a characteristic slit-like pupil that closes very narrowly, improving depth of field to catch prey and reducing the amount of light that could damage the retina. Big cats have pupils that contract to a round point instead.

At night in the field if you see reflective eyes staring back at you, it is likely a vertebrate with tapetum lucidum, a tissue that reflects light and enables animals to see in dim light. This is more common in nocturnal animals, so humans lack this eye structure. When light reflects off mineral crystals in the the tapetum lucidum it is called “eyeshine.” Cats, dogs, and raccoons have green eyeshine; coyote, rodents, opossums, and birds have red eyeshine, and many other mammals like horses have blue eyeshine. Some fish species have white eyeshine.
Animal eye structure has adapted to animal functions and environments.











