
Sampling
Sampling
It is usually impossible to study all of something. For example, it would not be possible to study all of the monarch butterflies. Sampling is a way to study a subset of organisms and then try to extrapolate to the larger population.
Learning Objective: Discuss the techniques, benefits, and limitations of sampling from a larger population.


Researchers rarely get the opportunity to sample an entire population, unless it is quite small, like an endangered species or a tiny habitat.
A sample is a smaller part that is intended to accurately describe the larger whole.
Sampling a small defined number of individuals and extrapolating the results to the larger population is a common practice in many fields.
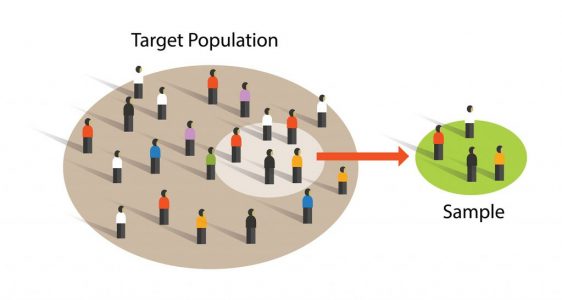
What is an advantage of sampling?
hint: if you were asked about characteristics of a grass species in a large lawn, what is the clear advantage of taking a smaller sample?
What is a potential disadvantage of sampling?
hint: think about if by chance you get something unusual in the sample, the assumption would be that whatever that is, is actually common.

A larger number of samples in an area typically provides a more accurate representation.
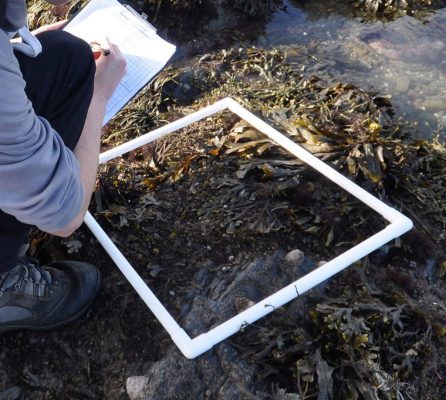

Resources (materials, time, money) and weather often limit sample number and sizes.

In our field work (streams for Lesley; lakes and forests for Mark), weather and time were often the limiting factor. As graduate students our labor costs were inexpensive, but the time window to collect seasonal data was narrow.
A quadrat is often used to delineate a consistently sized sampling area and can be inexpensive to construct.
Watch this video; you can select the closed captioning “cc” option if you would like to see the text.
Start Your 3A Media Assignment here
In this media assignment you are creating a data collection plan that you will use for media pieces 3B and 3C.
Choose a location with a population of organisms. It can be a yard, field, or somewhere indoors like a carpeted room. The species can be plant, animal, or fungus.
Determine the approximate size of the entire location/habitat, and the size of the smaller area you will sample at that location.
Design a quadrat to sample with, list any other supply needs, and identify potential safety issues.
We are providing the research questions that you will be supplying data to answer:
-
What is the population size? (population data is described in the next section)
-
How is the population distributed?
-
Is there evidence of interactions within the population and/or interactions of the population with other species?

Upload to Canvas a document that includes:
-
The name of the location that you will be sampling (can be map coordinates, name of a park, type of room, etc.)
-
The name of the organism you will be sampling (does not need to be an animal)
-
The approximate size of the overall location you are sampling.
-
The size of the smaller area you will sample at that location, including the design of the quadrat you will use to sample.
-
A list of any additional supply needs (you can just say its your field kit, if that is enough)
-
A list of any potential safety issues.
The next section introduces data on animal populations.











