
Temperature Control
Temperature Control
Animals have structures and behaviors to maintain a range of temperatures.
Learning Objective: Summarize the importance of temperature control, including different structures and behaviors animals use to maintain homeostasis.

Even with layers of clothing, heating, and air conditioning, we think about our temperature many times every day. Other species are also continually maintaining temperature.
Watch this video; you can select the closed captioning “cc” option if you would like to see the text.

Maintaining balance in the body is called homeostasis.
Similar to the idea of a thermostat, there is a set point or range, and there can be fluctuations around that point, but the mechanisms of the body typically try to keep fluctuations to a minimum.
Homeostasis in the human body (and many other vertebrates)
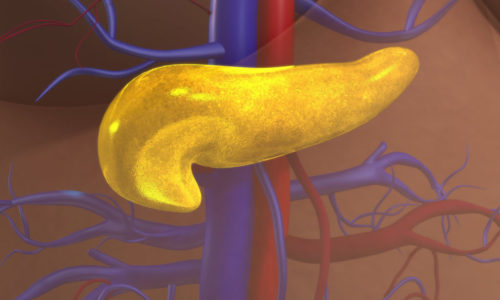
Blood Sugar
In humans, the pancreas releases hormones that maintain relatively constant levels of blood glucose
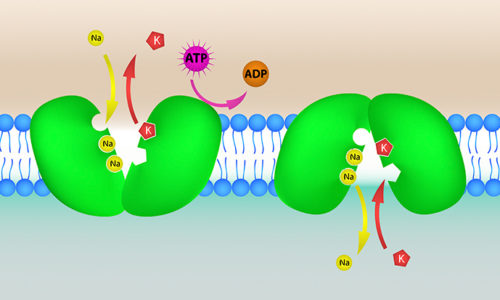
Sodium in Cells
Cells maintain their own balance through water and ion movement
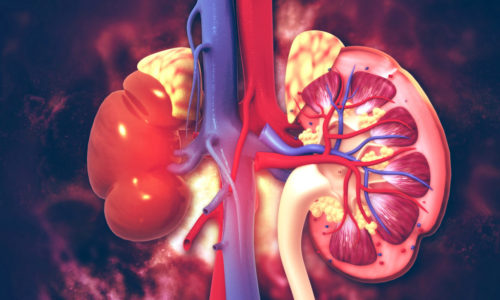
Blood Pressure
Nerves and hormones connecting multiple organs control blood pressure
Birds and mammals maintain a relatively constant internal body temperature. This form of homeostasis is called homeothermy, also known as “warm-blooded.” It takes continual burning of energy-containing molecules to maintain temperature, so even though birds and mammals can be active in the cold, they have to eat a lot of food to maintain temperature. This production of heat from within the body is called endothermy.


Most other animals, including reptiles, get much of their heat from their environment, a process called ectothermy. Ectotherms move from shade to sun, or underwater to basking on a rock to alter body temperature.
Ecto = outer
Endo = inner
Body structures can assist with heating or cooling.

Elephant Ears
Elephants not only use their large ears for exceptional hearing, they also flap them to dissipate heat.

Thick Fur
Sea otters continually groom their thick hair, maintaining an intact thermal barrier.
Penguins use a countercurrent form of blood circulation to keep their flipper extremities significantly cooler than their internal body temperature.
Some species of ecotherms, like these goldfish, can survive cool temperatures for short periods of time by moving slowly and longer periods of time by hibernating.
Hibernation as a form of temperature regulation will be covered in a later guide.
Animals use a combination of structures and behaviors to maintain homeostasis. We’ll explore other forms of homeostasis in upcoming modules.











