Evidence
Evidence
Science is based on observation and the collection of evidence.
Learning Objective: Distinguish between direct and indirect evidence, and provide examples of both.


Science is limited to observable phenomena, meaning there has to be evidence that something exists to be addressed by a science field. Evidence can be direct or indirect, both are critical in scientific inquiry.
Evidence enables researchers to support predictions. For example, a change in barometric pressure enables meteorologists to predict the weather will change.

Direct Evidence
Direct evidence is actually experiencing a phenomenon as it occurs, for example, watching an osprey catch a fish or smelling the scent of a skunk. This is taking in sensory information as a form of evidence.

Indirect Evidence
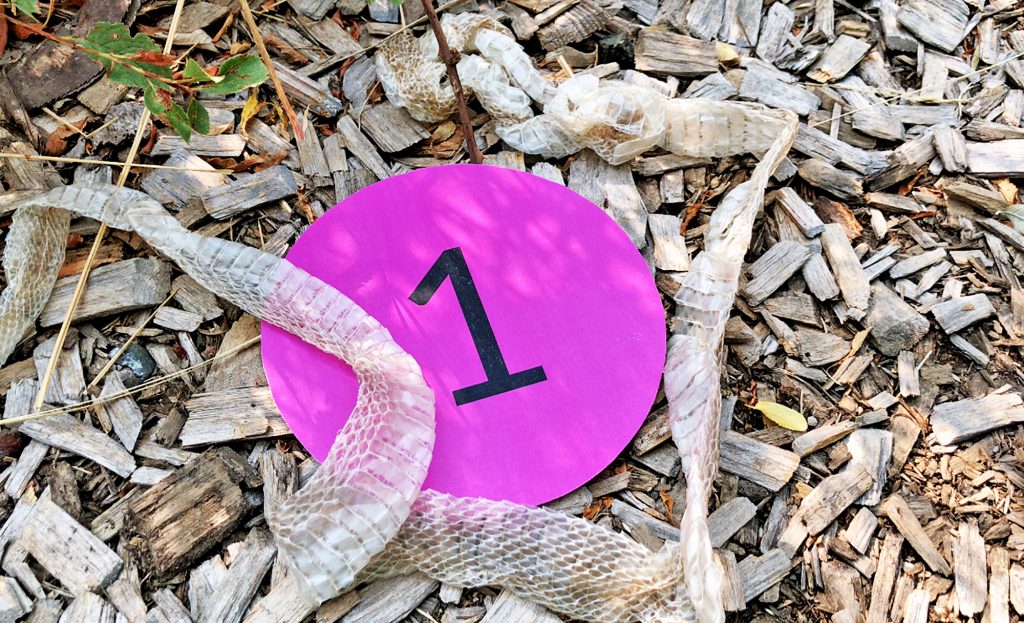
Indirect Evidence is collecting traces and objects created by something that happened at another time or place. Finding an animal track is indirect evidence that an animal was in the location.
We are surrounded by evidence of things occurring (direct) and things that have occurred (indirect).
In this video, Mark finds a variety of forms of evidence along our trail, including: tracks, scat (fecal material), insect damage, and structure building.
Watch this video; you can select the closed captioning “cc” option if you would like to see the text.
Indirect evidence is used to recreate an occurrence, the higher the quality and quantity of evidence, the more accurate the conclusions. Here is an example of indirect evidence in action.
Watch this video; you can select the closed captioning “cc” option if you would like to see the text.
Start Your Media Assignment here
In this section and the next four sections of this Identification Guide, you will view different forms of indirect evidence, including tracks, scat, and chews. For this media piece you are finding and submitting indirect evidence of animal activity. It can be indirect evidence of human activity if other animals are not available. This assignment is demonstrating the ability to recognize, collect, and interpret indirect evidence.
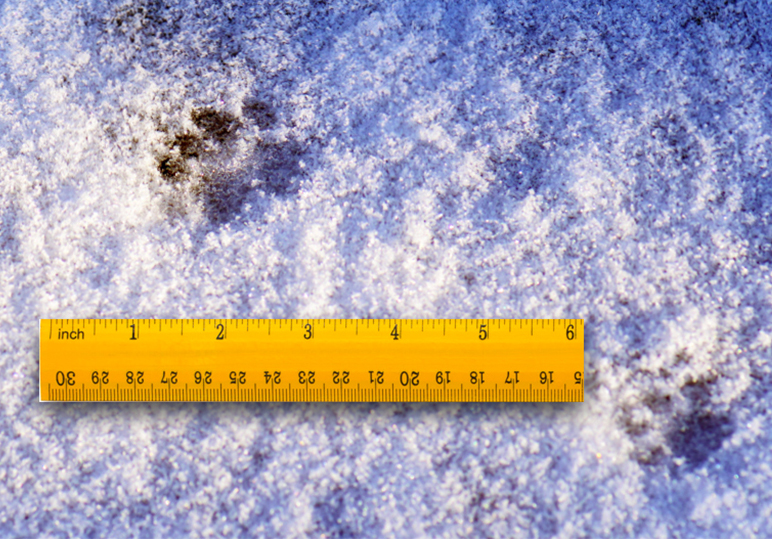

What you are submitting:
-
Indirect evidence of animal activity. It can be a single animal or a group. The evidence can be a photo, video, audio, sketch, or written description.
-
Include a brief description of how you found the evidence and what you believe the evidence represents. This can be added in the “comments” box, or incorporated into the media piece.
The next few sections introduce forms of indirect evidence of animal activity.