
Soil Organisms
Soil Organisms
Soil animals play a critical role in breaking down decaying organisms, part of organisms, and fecal material. Eventually these remains are broken down by fungi and bacteria into small enough particles that they can be recycled back to producers like plants and algae.
Learning Objective: Discuss methods for locating soil organisms and identify provided organisms by their taxonomic group and functional classification.


Taxonomic classification is naming organisms based on their structures like bones and teeth, and more recently their genetic structures as well.
Organisms are classified in one of three Domains that were introduced in the phylogenetic \”tree-of life\” video in guide 1A. The Domains are Bacteria, Archaea, and the Domain that animals are classified in, Domain ________.
The animal Kingdom has approximately 35 phyla, only one of these contains animals with backbones. Soil invertebrate animals represent multiple phyla.
Common Soil Organism Phyla

Phylum Annelidia
Segmented Worms
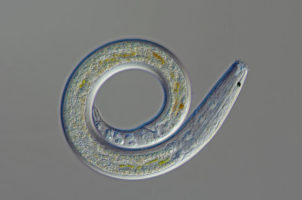
Phylum Nematoda
Microscopic Roundworms

Phylum Arthropoda
Jointed Appendages
Phylum Arthropoda, the arthropods, are species with jointed appendages, including antennae and legs.
The arthropods are broken into several groups or taxa.
Four Arthropod Taxa

Crustaceans
Diverse, many in water: barnacles, shrimp, crabs, sowbugs

Myriapods
Many Legs: includes millipedes and centipedes

Arachnids
Eight Legs: includes spiders and scorpions

Insects
Six Legs: includes beetles, bugs, crickets, and butterflies
Insect arthropods represent as estimated 90% of animal species on Earth, although many have not yet been discovered. New species are being located on a regular basis, particularly in species-rich rainforests and coral reefs.
Soil organisms, including these dermestid beetles and their larvae, scavenge (consume) dead organisms.
Note: beetle larvae are consuming an animal corpse
Introduction to soil organisms in a pile of composting lawn clippings and kitchen scraps.
Soil animals are critical in recycling nutrients though the food web.
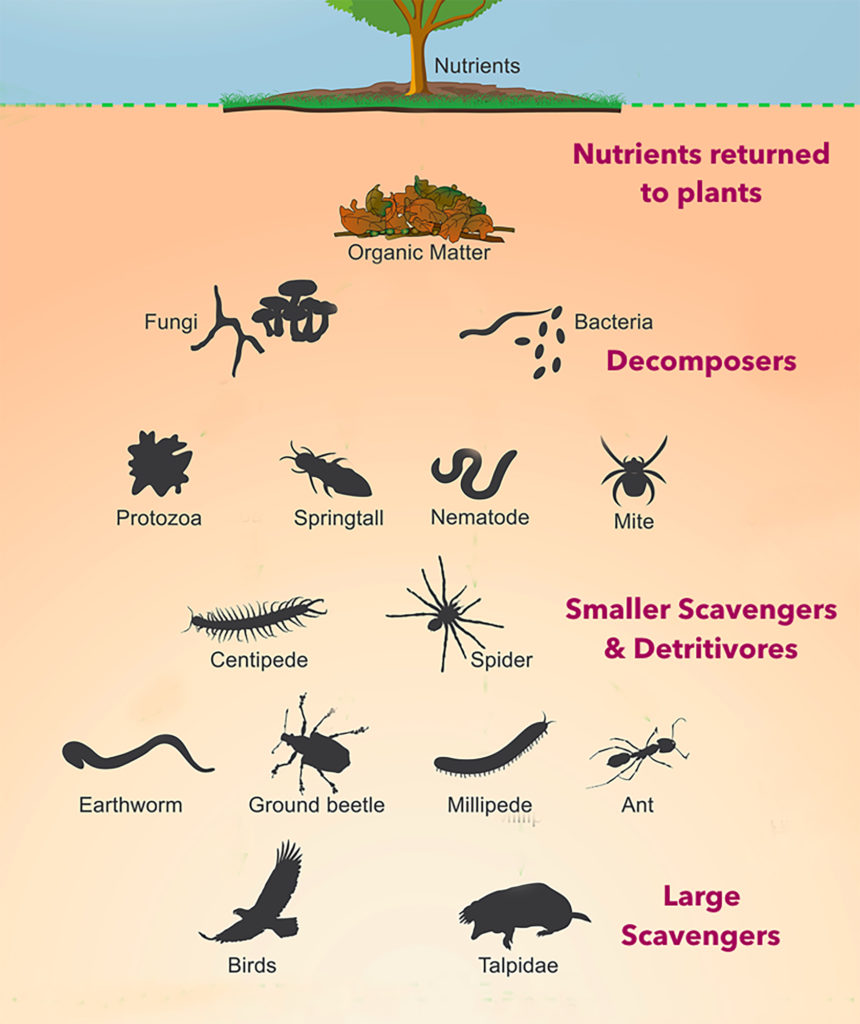
Consider the taxonomic classification of the soil animals in this video (for example, \”arthropod insects\” or \”annelid worms\”) as well as their functional classifications that are introduced.
Watch this video; you can select the closed captioning \”cc\” option if you would like to see the text.
From this page so far, Sowbugs are taxonomically classified as: ___________ and functionally classified as: ___________
Sowbugs breath with gills, so they are likely to be found in wet soils where they break down decaying organisms. They are found in many locations and are also easy to raise in an escape-proof damp terrarium with plenty of food and cover to hide under.
(answers: sowbugs are taxonomically classified as crustacean arthropods and functionally classified as detritivore consumers)
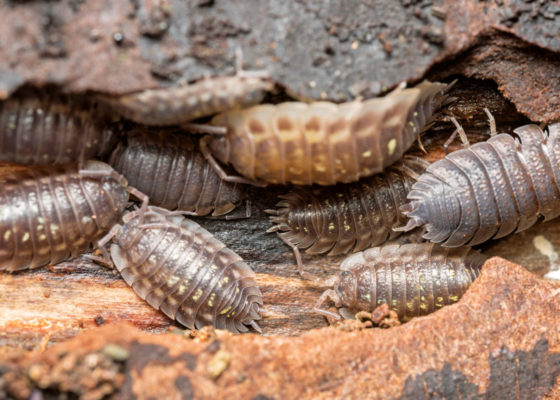
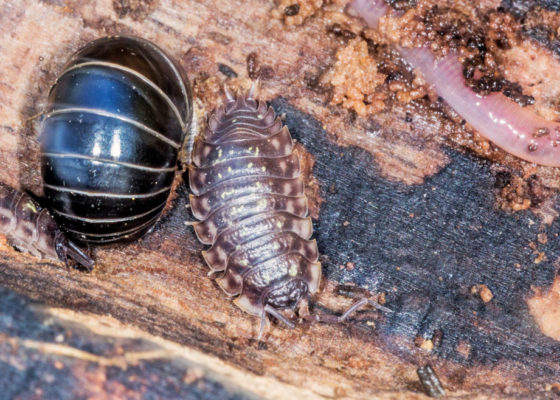


Sowbugs (center arthropod) are often confused with \”roly-poly\” pillbugs (left arthropod) that curl into a ball in response to potential predators. Sowbugs do not have this defensive movement, they just walk away quickly and try to get under something.
Sowbugs collected from along our yard path have increased dramatically in population size with addition of kitchen scraps.
Soil organisms can compete for food, watch the interactions between crickets and sowbugs. Which species appears to have a competitive advantage?
Watch this video; you can select the closed captioning \”cc\” option if you would like to see the text.
Throughout this course you will be introduced to animals you are likely to encounter in your field work. They fill a variety of functional roles in their ecosystems and have diverse feeding structures and behaviors suited for survival in unique habitats.











