
Cnidarians
Cnidarians
Cnidarians include the foundation species of coral reefs, forming intricate relationships with other species.
Learning Objective: Summarize the structural characteristics, representative organisms, and ecosystem significance of cnidarian species.

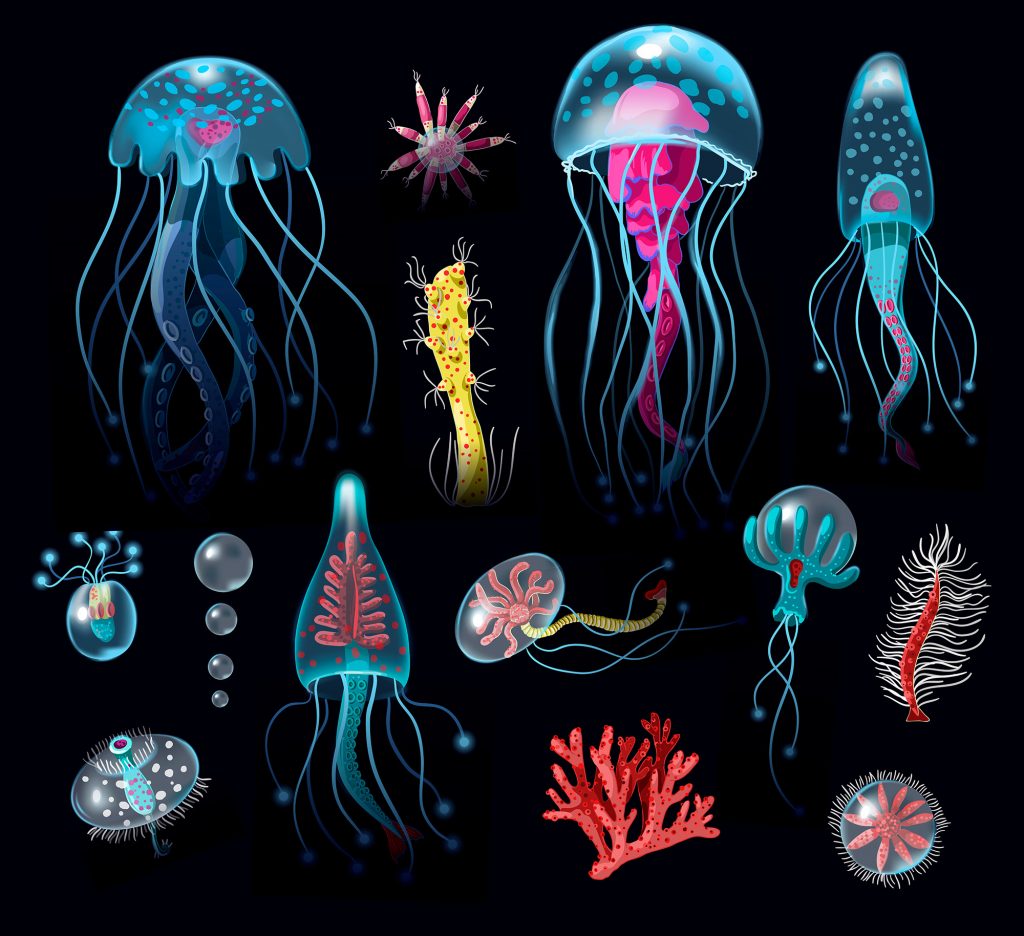
Phylum Cnidaria includes many well-known marine invertebrate species, including jellyfish, corals, and anemone.
Cnidarians have stinging cells called cnidocytes that have a trigger and a barbed hair-like extension than can inject toxins into potential prey.
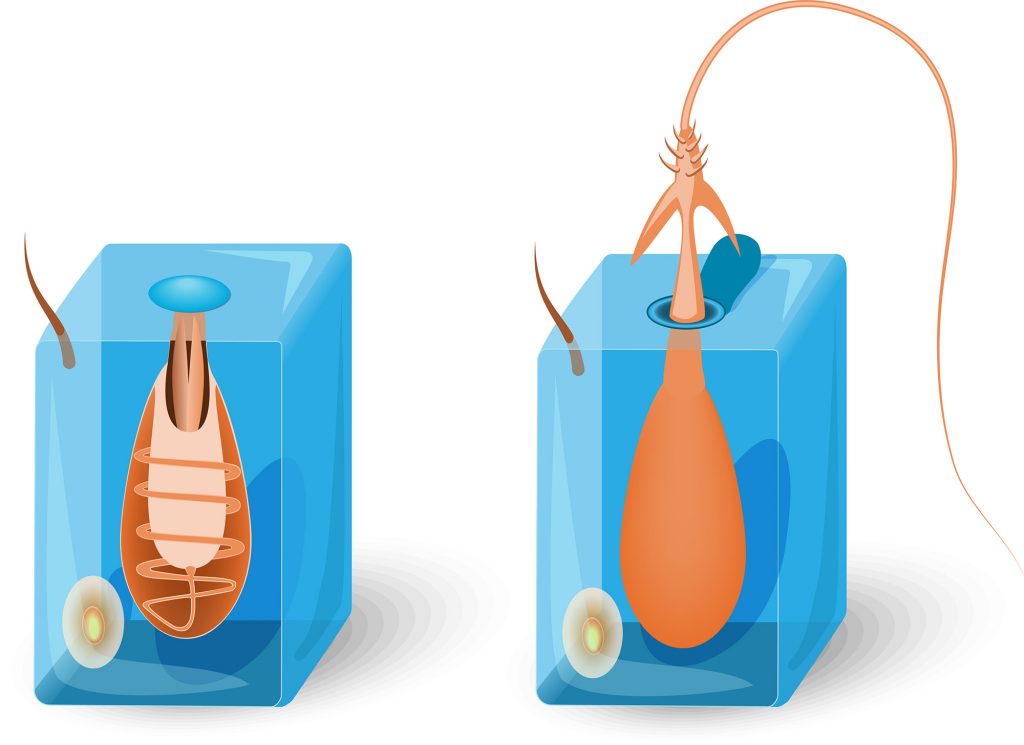

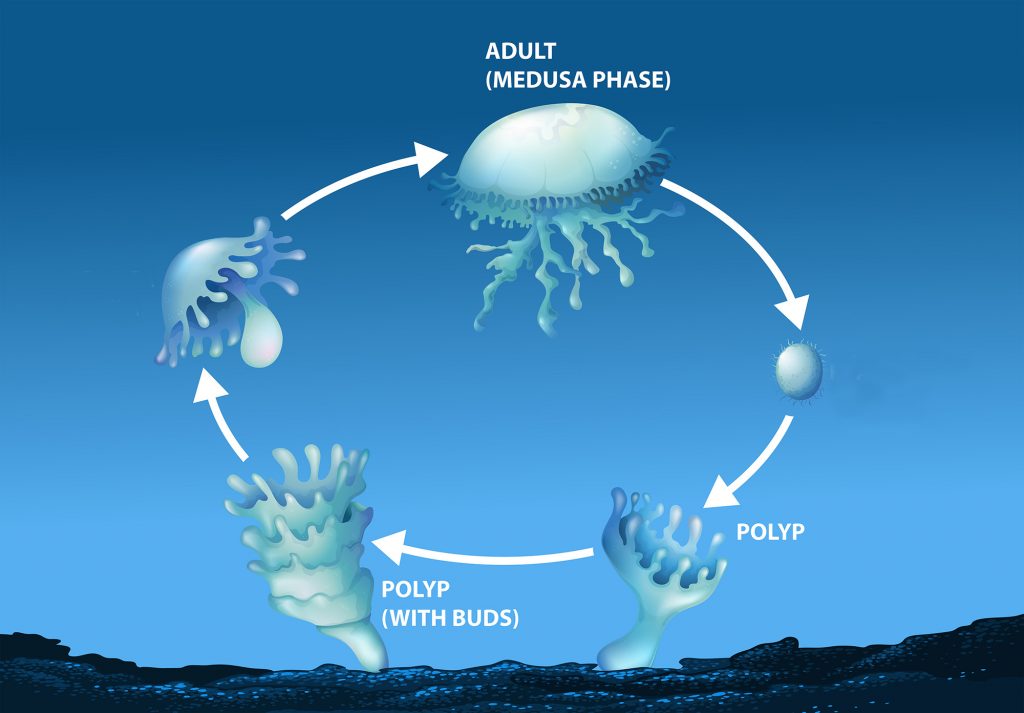
Many cnidarians have a polyp life stage when they are attached to a surface and a free-floating or swimming medusa stage where the body is shaped like a bell with trailing tentacles.
Jellyfish

Jellyfish are believed to be the oldest taxa of animals with organs, dating back as far as 700 million years ago. Sponges, animals without organs, go a bit further back in the fossil record.
Jellyfish typically have long tentacles that can catch food flowing through the water. These “upside down” jellyfish (Cassiopeia xamachana) lay bell side down in the sand and catch small organisms out of the water. Their tentacles have endosymbiotic zooxanthellae, and they orient them towards sunlight. The jellyfish get sugars, and the zooxanthellae get shelter and some nutrients from the jellyfish. Both species benefit, so this is an example of a _____ symbiotic relationship.
A group of jellyfish filtering water for food and pointing zooxanthellae-filled tentacles up towards the light.
Corals
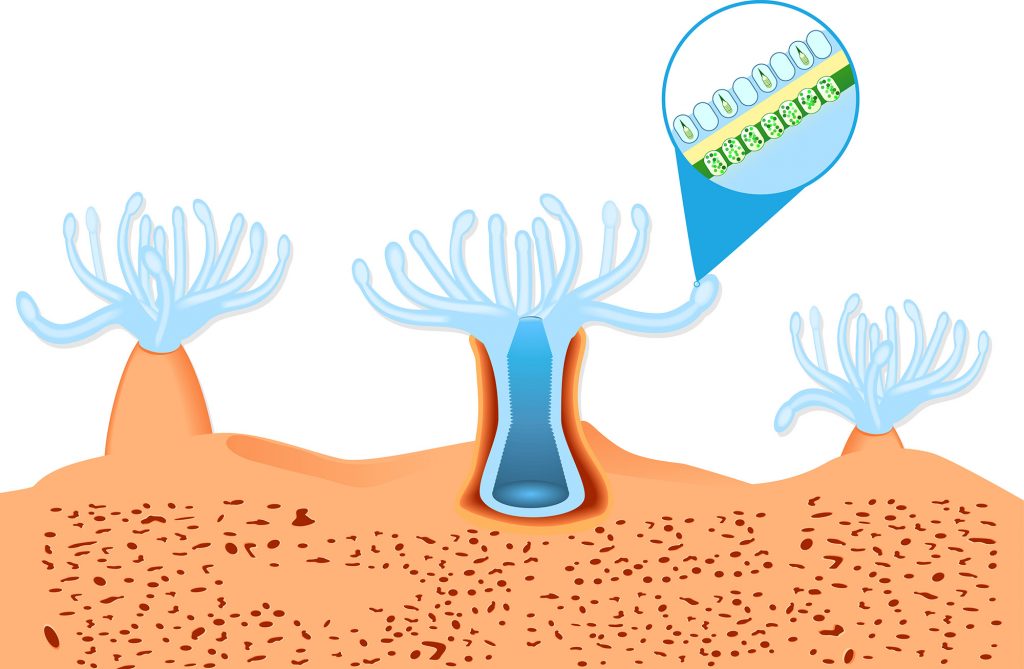
Coral animals have a critical endosymbiont: photosynthetic microorganisms called zooxanthellae.
This video introduces corals and coral reefs.
Watch this video; you can select the closed captioning “cc” option if you would like to see the text.
These videos show two different types of coral species. Both are a group of polyps, and each individual polyp has its own mouth and tentacles.
Anemone
Anemone often have endosymbiotic producers living in their bodies. The anenome species are found in cooler coastal waters, but resemble anemone found in warmer coral reefs.
This touch pool at the Hatfield Marine Science Center in Newport, Oregon is a comfortable way to study and make media about anemone.
Mark demonstrates a way to make a mediated experience more modal: gently handling an organism and describing the process.
Knowledge about cnidarians is needed to develop techniques for stabilizing the complex coral reef ecosystems.











