
Hormones
Hormones
Hormones are chemicals that cause cells to do things, often by altering protein production.
Learning Objective: Explain how hormones relate to genes and proteins, including how hormones impact animal behaviors.


When you think of a hormone, there are some familiar names like testosterone, estrogen, or growth hormone. All of these are chemicals that are released by cells that cause other cells to do things.
Hormone production is driven by genes, and there are similar genes (and hormones) across animal species.
This video introduces what hormones are and a few of their impacts.

Hormones can have a direct impact on animal behaviors. Research on rufous-winged sparrows (Peucaea carpalis) suggests that the amount of light received in a given day alters brain activity and hormone production. This appears to be the way they “know” when to mate and build nests: changing day lengths alter levels of a variety of hormones related to reproduction.
Frog mating calls have been linked to levels of androgens, hormones that are typically found in significantly higher levels in genetic male animals. Testosterone is an example of an androgen found in humans and other species; it plays an important role in structures and behaviors related to reproduction.

Hormones and Migration

When the Dusky Canada Goose leaves Alaska to head to its winter grounds in the Willamette Valley of Oregon, it has already undergone a series of hormonal changes. These changes include increased appetite to build stored energy for flight and increased activity or “agitation” that makes migration more likely.
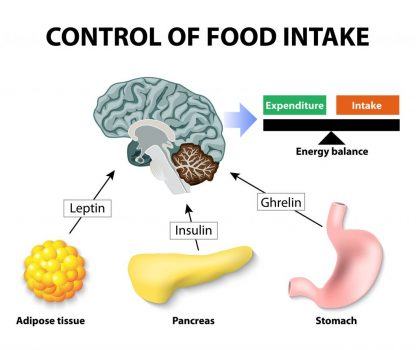
Migratory birds often increase food consumption prior to migration and then suddenly simultaneously have decreased appetite and increased restlessness. This has been linked to increases in the hormone ghrelin, an appetite-regulating hormone also found in humans.
The next section introduces a group that contains some of the most impressive migratory species: marine mammals.











